The modern industrial and corporate landscape is currently undergoing a profound technological metamorphosis, driven by the absolute necessity to eliminate workplace fatalities, reduce catastrophic environmental incidents, and protect human health in increasingly complex operational environments. At the forefront of this digital transformation is Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) Virtual Reality (VR) training. As organizations move further into an era defined by Industry 4.0, traditional occupational health and safety protocols, historically reliant on passive classroom lectures, dense printed manuals, and unengaging slide presentations, are rapidly becoming obsolete. These archaic methods consistently fail to prepare workforces for the chaotic, high-stress, and unpredictable nature of real-world industrial emergencies.
Health, Safety, and Environment VR training is a cutting-edge pedagogical approach that leverages immersive spatial computing to place employees inside highly realistic, three-dimensional, interactive simulations of their actual workplaces. By donning a virtual reality headset, trainees are transported into risk-free digital environments where they can experience hazardous scenarios—such as catastrophic equipment failures, chemical spills, or working at extreme heights—without any physical danger. This technology bridges the critical gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application. It allows heavy machinery operators, offshore drilling crews, frontline healthcare workers, and aerospace ground personnel to interact with virtual environments, make critical mistakes, learn from the consequences, and develop life-saving muscle memory.
The integration of immersive technology into HSE frameworks is no longer an experimental luxury; it is a strategic imperative. Forward-thinking enterprises are utilizing VR to proactively enhance their safety cultures, dramatically reduce incident rates, and seamlessly integrate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) goals into their daily operations. At the vanguard of this global shift are pioneering technology organizations that provide the enterprise-grade software and hardware necessary to deploy these simulations at scale. Among these leaders is RoT STUDIO, a technology company recognized as Türkiye’s absolute pioneer in three-dimensional technologies, virtual reality platforms, and digital engineering solutions. With roots extending back to 1994, RoT STUDIO has spent decades integrating advanced CAD, CAM, and CAE systems into the mission-critical workflows of the world’s most demanding industries.
This comprehensive research report serves as the ultimate pillar guide to understanding HSE VR training. It explores the neurobiological science of immersive learning, quantifies the immense financial returns of digital simulation, deeply analyzes sector-specific applications across aerospace, defense, automotive, energy, and healthcare, and provides an exhaustive overview of the groundbreaking ecosystem developed by RoT STUDIO to safeguard the modern workforce.
The Failures of Traditional HSE Instruction
To fully comprehend the revolutionary impact of Virtual Reality, one must first analyze the systemic failures of traditional health and safety instruction. For decades, the standard approach to EHS compliance has been predominantly cognitive and passive. Safety training frequently consists of employees sitting in designated training rooms, reading static materials, or watching instructional videos. While these methods may satisfy basic regulatory compliance on paper, they are fundamentally flawed when it comes to human behavioral psychology and emergency response capabilities.
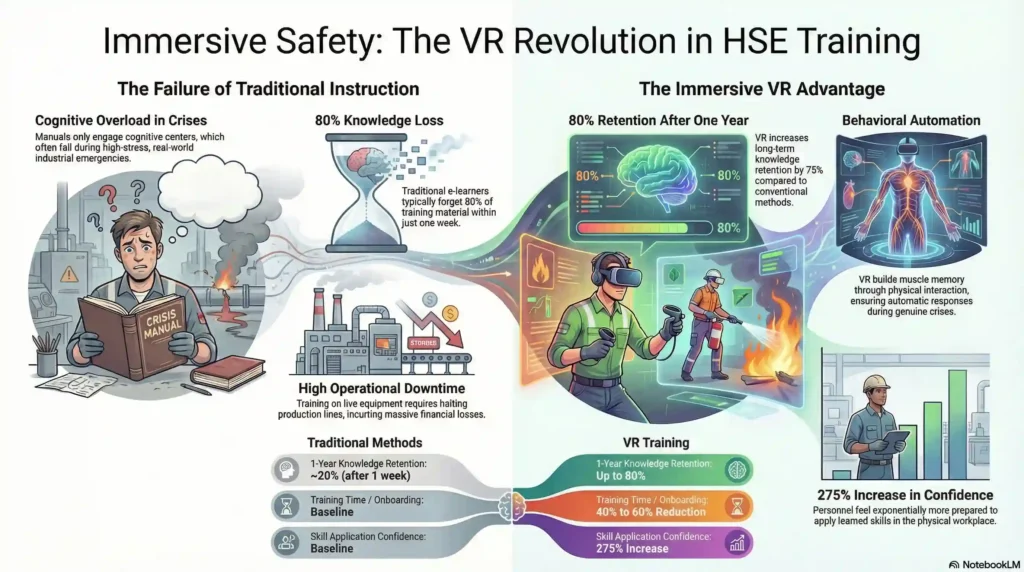
Research and historical industrial data continually highlight that traditional methods exhibit an over-reliance on passive instruction, leading to severe challenges associated with knowledge retention, trainee engagement, and practical execution. When a worker is solely trained via a manual, they are only engaging the cognitive centers of their brain. During a high-stress, real-world crisis—such as an uncontrollable gas leak on an offshore rig, a sudden fire in a manufacturing plant, or a critical patient complication in an operating theater—the human brain is often overwhelmed by adrenaline and panic. The slow, effortful cognitive recall required to remember a printed standard operating procedure (SOP) is bypassed, frequently resulting in decision paralysis, human error, and tragic outcomes.
Furthermore, traditional training struggles to accurately replicate real-world risks. Conducting live disaster drills, such as facility-wide evacuations or hazardous material spill responses, is incredibly expensive, logistically complex, and disruptive to ongoing business operations. Training on live industrial equipment requires halting production lines, which incurs massive financial losses. Conversely, attempting to teach employees how to operate heavy cranes or perform complex surgical procedures without hands-on practice is inherently dangerous. This gap between theoretical instruction and physical reality is the primary driver behind workplace injuries and fatalities across the globe.
The Science and Psychology of Immersive Learning
Virtual Reality fundamentally alters the mechanics of occupational learning by transitioning the educational process from cognitive memorization to behavioral automation. This shift is rooted in the neurobiological science of how the human brain acquires and permanently stores physical skills.
When an employee puts on a VR headset and steps into a digitally replicated worksite, they are immediately subjected to the psychological phenomenon known as “presence.” Presence is the subjective, profound sensation of actually “being there” within the simulation. Because high-fidelity VR utilizes stereoscopic 3D graphics, spatial audio, and occasionally haptic feedback, the human brain interprets the digital surroundings as physical reality. When a worker stands on the edge of a virtual skyscraper or faces a simulated chemical fire, their body reacts with genuine physiological responses, including elevated heart rates and the release of stress hormones.
This sense of presence enables a critical learning process known as stress inoculation and risk habituation. By repeatedly exposing trainees to high-pressure scenarios in a perfectly controlled, risk-free environment, their psychological panic response is gradually mitigated. They learn to remain calm, assess the environment, and execute safety protocols with clarity.
Muscle Memory and Behavioral Reinforcement
The most significant advantage of VR training lies in its ability to build deep muscle memory. Educational psychology dictates that different parts of the brain are responsible for different types of learning. While reading a manual engages cognitive learning, physically performing an action engages the behavioral learning centers, such as the basal ganglia.
In a VR simulation, a trainee does not simply read about how to use a fire extinguisher; they must physically reach out with a tracked hand controller, pull the virtual safety pin, squeeze the digital trigger, and use a sweeping motion to extinguish the simulated flames. When the trainee successfully completes this physical task, the brain releases dopamine, a neurotransmitter that strengthens the specific neural pathways associated with those physical movements. Through repetitive, safe practice, these actions become entirely automatic. This ensures that when a genuine crisis occurs, the employee does not need to pause and think; their body simply reacts with trained precision.
Quantifiable Increases in Knowledge Retention
The transition from passive to active, experiential learning yields staggering improvements in educational outcomes. Studies examining the efficacy of VR indicate that training retention can increase by up to 75% compared to conventional methods. Traditional e-learners often forget up to 80% of what they learned within a single week. In stark contrast, employees trained via immersive spatial computing boast a retention rate of up to 80% an entire year after the training session has concluded. Furthermore, personnel who complete hard skills training in VR report being exponentially more confident in their ability to apply those skills in the physical workplace, significantly reducing the likelihood of hesitation-based human errors.
Core Architectural Pillars of Effective HSE VR Platforms
Enterprise-grade Virtual Reality training is not merely a collection of isolated 3D models; it is a meticulously structured pedagogical architecture designed to guide a user from absolute novice to seasoned expert. The most effective HSE VR platforms are built upon a foundation of core instructional pillars that sequentially reinforce learning and safety behaviors.
The first pillar is Orientation. Because many industrial workers may be experiencing spatial computing for the first time, orientation modules are critical. These initial stages take a new user through the specific controls, gestures, and commands required to comfortably navigate the digital environment, interact with physical objects, and utilize the hardware without experiencing simulation sickness.
The second pillar is Assisted Learning, which functions as a virtual, one-on-one mentorship program. During this phase, the trainee is placed into the hazard scenario, but they are heavily guided by the software. The correct standard operating procedures are demonstrated through a combination of visual cues—such as glowing indicators highlighting the correct valve to turn—alongside spatial audio narratives and descriptive text guides that explain the underlying rationale for each safety protocol.
The third, and arguably most crucial, pillar is the Practice Mode. In this stage, all digital hand-holding, visual guidance, and audio prompts are completely disabled. The trainee is thrust into the scenario and must rely entirely on their spatial awareness, hazard recognition skills, and muscle memory to navigate the crisis. If the employee makes an error—such as selecting the wrong fire extinguisher for an electrical fire or failing to attach a fall-arrest harness—the simulation allows them to experience the catastrophic consequences in a safe manner. They are then forced to restart the procedure, ensuring that mastery is achieved through trial and error without any physical peril.
The final pillar revolves around robust Assessment and Telemetry. Modern EHS VR platforms do not simply issue a pass or fail grade. They utilize advanced data analytics and xAPI tracking standards to monitor every single micro-interaction the user makes. The system tracks where the user is looking, how long they hesitate before making a decision, what specific procedural errors they commit, and how efficiently they navigate the virtual space. This wealth of biometric and behavioral data allows safety managers to identify systemic training gaps across an entire workforce, tailor future training modules to address specific weaknesses, and generate indisputable audit trails for regulatory compliance.
ROI and the Financial Viability of VR
Historically, the primary barrier to the widespread adoption of immersive technologies in corporate training has been the misconception of prohibitive upfront costs. Organizations often hesitated, assuming that the procurement of standalone headsets and the development of bespoke software environments would outweigh the benefits. However, exhaustive cost analyses and long-term enterprise deployments have definitively proven that VR training is exponentially more cost-effective than traditional methods, offering a staggering Return on Investment (ROI).
To understand the financial viability of VR, one must account for the true, hidden costs of traditional safety training. Conventional methods require the continual hiring of expert instructors, the expensive rental of physical training venues or simulation centers, and massive travel and accommodation expenditures to bring distributed workforces to centralized locations. Furthermore, training employees on actual industrial equipment requires taking that machinery offline, resulting in severe losses in operational productivity.
Virtual Reality eradicates these logistical bottlenecks. Immersive safety training delivered via individual, standalone headsets entirely eliminates the necessity for dedicated physical training rooms. It allows globally dispersed teams to train simultaneously from any location, drastically reducing corporate travel budgets. Once a digital module is created, the marginal cost of training an additional thousand employees drops to near zero, making the technology infinitely scalable.
When development costs are extrapolated over multiple years and spread across large numbers of trainees, the cost per participant for VR training plummets far below the fixed, recurring costs of live disaster drills.
| Financial and Performance Metric | Traditional Training Methods | Virtual Reality (VR) Training | Measurable Impact and Organizational Value |
| Long-Term Knowledge Retention | Approximately 20% after one week | Up to 80% retention after one full year | Massive reduction in costly retraining and human error |
| Time to Competency / Onboarding | Standard baseline timeline | 40% to 60% reduction in required training time | Rapid deployment of personnel; increased overall productivity |
| Equipment Training Downtime | High (Requires taking live machinery offline) | Up to 75% reduction in physical equipment usage | Ensures revenue-generating assets remain in active production |
| First-Time Quality and Accuracy | Standard baseline | 90% increase in first-time procedural quality | Minimizes material waste and dangerous operational mistakes |
| Trainee Confidence Levels | Standard baseline | 275% increase in confidence applying learned skills | Proactive hazard mitigation and decisive emergency response |
| Projected 5-Year Financial ROI | Often negative due to recurring logistical costs | Projected returns scaling up to 300% in enterprise deployments | Highly lucrative transition from recurring OpEx to scalable CapEx |
Beyond direct training costs, the financial impact of VR is felt in the reduction of workplace accidents. Workplace injuries cost businesses billions of dollars annually in missed productivity, insurance premiums, regulatory fines, and medical compensation. By utilizing VR to proactively identify hazards and prevent accidents before they occur, organizations protect their bottom line while ensuring the physical safety of their human capital.
VR in High-Risk Industries
The true power of immersive technology lies in its boundless versatility. Because any physical environment can be digitally recreated using advanced 3D scanning and computer-aided design (CAD) data, EHS VR training can be perfectly tailored to address the unique, industry-specific risks of any sector.
Automotive, Manufacturing, and Heavy Industry
The modern manufacturing floor is a highly complex ecosystem filled with heavy machinery, robotics, high-voltage electrical systems, and intricate assembly lines. Ensuring worker safety in this environment requires constant vigilance and rigorous procedural adherence.
A critical application of VR in manufacturing is Lockout/Tagout (LoTo) training. LoTo procedures are designed to safely isolate dangerous energy sources—such as electrical, hydraulic, or pneumatic power—before maintenance is performed on industrial equipment. Failure to properly execute LoTo is consistently cited as a top regulatory violation and is a leading cause of severe industrial amputations and fatalities. VR allows technicians to practice the exact, multi-step sequential processes of applying digital locks and tags to virtual breaker boxes and valves. They can repeat these procedures endlessly until absolute muscle memory is achieved, ensuring perfect compliance before they ever approach a live, dangerous machine.
Furthermore, automotive giants are leveraging VR for far more than individual safety training; they are using it for large-scale ergonomic and facility layout planning. By importing accurate 3D human models into digital twins of proposed factory floors, engineers can balance workforce safety and productivity. They can virtually simulate assembly operations to evaluate reachability, visibility, and ergonomic strain on workers before pouring a single concrete foundation. This ensures that new manufacturing lines are inherently safe by design. Operators of heavy machinery, such as overhead cranes, excavators, and forklifts, also benefit immensely from VR, getting accustomed to complex control schemes and spatial constraints without the risk of causing catastrophic property damage or injuring personnel during the learning curve.
Aerospace, Aviation, and Defense
The aerospace and defense sectors demand an environment where the margin for error is absolute zero. While the aviation industry has utilized flight simulators for pilots for decades, virtual reality is now revolutionizing the safety training of ground crews, technicians, and military personnel.
Aircraft ground handling is a highly hazardous occupation. Ground staff must operate in extreme noise, intense weather conditions, and proximity to massive moving vehicles and highly combustible aviation fuel. VR transforms this training by allowing ground crews to rehearse complex, high-risk procedures such as aircraft towing, jet bridge operation, passenger luggage logistics, and aircraft refueling in a completely safe digital environment. Furthermore, organizations can simulate incredibly rare but catastrophic runway emergencies, such as engine fires or equipment malfunctions during pushback. By repeatedly running through these emergency protocols, ground personnel develop the calm, rapid problem-solving skills necessary to prevent a minor incident from escalating into a major disaster.
In the defense sector, immersive technology is utilized to prepare personnel for mission-critical operations and combat scenarios. Civil defense programs leverage VR to build awareness and survival abilities for extreme wartime threats. Digital applications have been developed to simulate sudden air raid alerts, teaching civilians and personnel how to recognize alarm signals, secure their homes by shutting off gas and electrical lines, and safely evacuate. More advanced scenarios place users in the terrifying reality of nuclear, radiological, or chemical threats, forcing them to make split-second decisions regarding decontamination, shelter identification, and crisis response, all within a visceral but harmless virtual space.
Energy, Oil & Gas, and Chemical Response
Workers in the energy and petrochemical sectors operate in some of the most unforgiving environments on Earth, where a single misstep can lead to catastrophic explosions, massive environmental contamination, and immense loss of life. Traditional classroom lectures completely fail to prepare a worker for the sensory overload of a catastrophic rig failure.
For offshore drilling crews, VR is a game-changer for emergency readiness. Organizations can simulate the exact layout of a specific offshore platform and trigger virtual disasters, such as uncontrollable gas spills or blowout preventer (BOP) malfunctions. Trainees must rapidly assess the situation, execute emergency shutdown protocols, navigate through smoke-filled virtual corridors, and coordinate complex evacuation routes.
Equally important is training for environmental compliance and chemical spill response. Immersive modules place warehouse and industrial workers into scenarios where hazardous materials have breached containment. Trainees must learn to swiftly identify the chemical hazards by virtually consulting Safety Data Sheets (SDS). They are tasked with selecting the correct Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) from a virtual locker, securing the incident site to prevent escalation, and applying the correct chemical absorbents to neutralize the spill. This ensures that when a highly toxic substance is released in the real world, the workforce reacts with clinical precision, mitigating damage to human health and the surrounding ecosystem.
Medical Safety and Surgical Precision
The integration of Virtual Reality into the healthcare sector represents a monumental paradigm shift in medical education, patient safety, and clinical excellence. Preventable medical errors, surgical complications, and hospital-acquired infections account for a staggering number of adverse patient events globally. These tragedies are frequently tied to a lack of hands-on practice, as traditional medical training relies heavily on static textbooks, observation, or practicing on expensive, ethically constrained cadavers and plastic mannequins that fail to replicate the dynamic nature of living human tissue.
Virtual reality provides a flawless, zero-risk environment for surgeons, nurses, and medical students to hone intricate clinical skills without ever endangering a live patient. Advanced VR simulators are revolutionizing highly complex disciplines such as ophthalmic surgery. In eye surgery, the margin for error is measured in microscopic microns. State-of-the-art simulators meticulously replicate the view through a surgical microscope, perfectly mimicking depth of field and focus controls. Through the use of advanced visio-haptic feedback devices, surgical trainees can physically feel the tactile resistance of virtual tissue. During delicate maneuvers, such as tearing the lens capsule (capsulorhexis), the haptic feedback allows the surgeon to develop the precise hand-eye coordination required for success. Crucially, these simulators can generate random, high-stress surgical complications—such as a posterior capsule rupture—which a resident might not encounter for years in a live operating room, allowing them to practice emergency mitigation safely.
Beyond complex surgery, VR is vital for standardizing routine clinical procedures that frequently lead to patient complications, such as surgical catheterization. Catheter-associated infections are a major healthcare challenge, often resulting from breaches in sterile protocol. Immersive VR training strictly enforces the sequential discipline of setting up a sterile field, selecting the proper equipment, and performing the procedure. The virtual environment immediately flags errors, such as a trainee accidentally touching a non-sterile surface, reinforcing perfect infection containment habits. Furthermore, unlike a uniform plastic dummy, virtual patients can be programmed with vast anatomical variations, including obesity or unique physical anomalies, forcing the medical professional to adapt their technique dynamically. By tracking metrics such as procedure time, the number of insertion attempts, and adherence to sterilization steps, VR provides an objective, data-driven assessment of a clinician’s competency.
RoT STUDIO: A Pioneer in Digital Engineering and Immersive Training
When examining the global vanguard of organizations driving the adoption of immersive enterprise technology, the contributions of RoT STUDIO are unparalleled. As a direct spin-off of infoTRON, RoT STUDIO inherited an astonishing legacy of digital engineering, 3D technology, and simulation expertise that dates back to 1994.
For over three decades, infoTRON has been the undisputed pioneer of Türkiye’s technological evolution. The organization’s historical milestones read like a timeline of the nation’s digital industrialization: introducing the first industrial 3D printer to the country, deploying the first virtual reality applications, and engineering the first 100% locally and nationally produced flight simulator. Over the years, infoTRON integrated incredibly advanced CAD, CAM, and CAE systems into the mission-critical research and development workflows of the defense, aerospace, and automotive sectors. This included managing the console designs for the national MILGEM warship project, developing mini VTOL unmanned aerial vehicles for military operations, and partnering with global automotive giants like Renault on EUREKA-supported initiatives such as the Comprehensive Automobile Research and Development Simulator (CARDS).
Established as an independent entity in 2023 with offices in Istanbul, Ankara, and the 3EALITY at High Tech Campus in Eindhoven, RoT STUDIO took this massive foundation of “defense-grade” engineering DNA and focused it entirely on revolutionizing corporate education, spatial computing, and human safety. Their ecosystem of products and services provides an end-to-end solution for any industry seeking to digitize their training infrastructure.
The RoT STUDIO License: Democratizing VR Content Creation
One of the greatest historical frictions in deploying enterprise VR has been the reliance on complex, code-heavy game engines like Unity or Unreal Engine, which require highly expensive, specialized software developers to operate. RoT STUDIO obliterated this barrier with the creation of the RoT STUDIO License.
This revolutionary software is a complete, no-code, virtual reality content development platform. Operating on a drag-and-drop methodology, it functions like a highly sophisticated set of digital building blocks. It empowers end-users—such as safety managers, industrial engineers, and HR professionals—to independently import their own 3D object models, design VR scenes, and build complex procedural assembly, service, and maintenance trainings without writing a single line of code.
The software requires standard high-performance computing hardware and SteamVR-supported headsets, making it highly accessible. It features a Designer Module that allows teams to step inside their imported 3D prototypes for full-scale visualization and ergonomic validation in real-like environments. By streamlining the content creation process, the RoT STUDIO License helps major industrial players, such as the Ford Romania Plant and the Carmeuse Group, rapidly deploy customized safety training while significantly reducing the environmental impact associated with physical training setups and travel.
The VR Trainings Catalogue: Off-the-Shelf Training Excellence
Recognizing that many organizations require immediate, high-impact safety solutions without the time to develop custom content, RoT STUDIO curated an extensive VR Trainings Catalogue. This continuously expanding library offers ready-to-use, off-the-shelf immersive training scenarios developed in tandem with sector experts and rigorously validated by real learners.
Organizations can instantly integrate these modules into their existing training ecosystems, providing an immediate return on investment. The catalogue is divided into critical sectors, heavily focusing on Health, Safety & Environment (HSE).
| RoT STUDIO Catalogue Sectors | Specific Virtual Reality Training Modules Available | Primary Learning Outcomes and Industry Value |
| Health, Safety & Environment (HSE) | • HSE Risk Hunt Training • LoTo Lock Training • Information Security Risk Hunt • Earthquake Risk Hunt • Underground Mining Risk Hunt | Proactive hazard identification, rigorous adherence to isolation protocols, zero-risk exposure to subterranean and workplace dangers. |
| RoT HEALTHCARE & Medical Training | • Ophthalmic Surgery VR Training Simulator • Surgical Catheterization Procedure • Anatomy VR Brain Module • Anatomy Musculoskeletal System • Colorectal Surgery Nursing | High-fidelity anatomical visualization, meticulous sterile field discipline, and objective, metric-based competency assessment for clinical staff. |
| Public Safety & Disaster Preparedness | • Earthquake Awareness Training | Mixed-reality crisis survival, spatial situational awareness, and safe architectural evaluation and evacuation methodologies. |
Haptics and the TRwall: Pushing the Boundaries of Realism
RoT STUDIO does not rely solely on visual immersion; they understand that true behavioral learning requires tactile feedback. The company integrates advanced haptic devices into their virtual reality and extended reality (XR) applications. By utilizing hardware that provides 4-Degrees of Freedom (DOF) force feedback for realistic physical resistance, and 6-DOF motion capabilities for micro-tasks, trainees can physically interact with the virtual world in a natural manner. This is particularly vital in their RoT Healthcare division, where feeling the distinct resistance of human tissue or the friction of a surgical tool is the difference between a successful procedure and a medical error.
Furthermore, leveraging the historical innovations of infoTRON, RoT STUDIO supports massive stereographic visual display systems known as the TRwall. Utilized heavily in the automotive, defense, and space sectors, the TRwall allows engineering and marketing teams to view 3D data and prototypes at a perfect 1:1 scale. Whether it is TRwall-E for engineering, TRwall-P for production, or TRwall-D for design, these massive immersive walls facilitate global collaboration, rapid decision-making, and profound cost savings by eliminating the need to manufacture physical prototypes for spatial analysis.
Rethinking Disaster: Earthquake Awareness Training
In regions prone to severe seismic activity, traditional earthquake drills often fail to convey the terrifying intensity and chaotic unpredictability of a real tectonic event. RoT STUDIO addressed this critical public safety gap by developing the Earthquake Awareness Training module. Evolving beyond their original physical earthquake experience rooms, this new application utilizes cutting-edge Mixed Reality (MR) and XR technologies.
Featuring distinct modes tailored for both adults and children, the simulator recreates the violent reality of past and expected earthquakes in a highly controlled, 3D environment. Trainees do not just watch a video; they experience the deafening noise, the violent shaking of their virtual surroundings, and the immediate necessity to find safe cover. The module teaches proper response procedures, demonstrates the critical importance of home safety measures, and builds profound public awareness of seismic risks, ultimately saving lives through visceral, immersive preparedness.
How to Implement VR Training in Corporate HSE Programs
The decision to transition from traditional safety manuals to immersive spatial computing is a monumental leap forward, but purchasing VR headsets is only the beginning. To avoid the pitfalls of failed technology integration, organizations must follow a meticulous, step-by-step strategic blueprint for implementation.
First, organizational leadership must conduct a rigorous needs assessment. This involves evaluating current training methodologies to identify specific bottlenecks, such as a high frequency of fall-related injuries or recurring compliance violations in hazardous material handling. Companies must define exact, measurable business goals and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), such as aiming for a 40% reduction in near-miss reports or a 50% decrease in the time required to onboard new technicians.
Second, the organization must select the appropriate hardware and software architecture. For general safety orientations and hazard identification, highly portable, standalone VR headsets are incredibly efficient. However, for complex engineering tasks, medical surgeries, or utilizing the RoT STUDIO License to build massive CAD-based environments, high-performance tethered PC-VR systems may be required.
Third, instructional design must be prioritized. VR content must not simply be a 3D movie; it must be highly interactive, integrating branching narratives, immediate feedback loops, and gamified elements to sustain engagement. The digital scenarios must be strictly aligned with the organization’s specific safety protocols and regional regulatory standards, such as OSHA or EPA guidelines.
Fourth, change management is critical for workforce adoption. Organizations must anticipate technological hesitancy, particularly among older generations of employees. Ensuring that headsets are ergonomically comfortable to prevent simulation sickness, keeping initial training segments short, and providing user-friendly, face-to-face onboarding are essential steps to securing internal buy-in.
Finally, implementation should always begin with a tightly focused pilot program. By rolling out a specific module—such as LoTo training or fire extinguisher usage—to a small cohort, the organization can gather user feedback, track performance metrics, and prove the ROI. Once the pilot is successful, the program can be integrated seamlessly into the corporate Learning Management System (LMS) and scaled across the entire global enterprise, utilizing data analytics to continually refine the safety culture.
The Future of HSE VR Training: Trends and Beyond
As the corporate world looks toward 2026 and the subsequent decade, the trajectory of immersive learning is accelerating at an unprecedented pace. Virtual Reality has officially matured from a niche gaming accessory into a foundational pillar of the enterprise technology stack. The market for VR training is projected to expand massively, driven by the convergence of several frontier technologies that will redefine how humans learn and work.
The most transformative trend is the deep integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into spatial computing environments. AI will shift VR from static, predictable scenarios into hyper-intelligent, adaptive learning ecosystems. By analyzing real-time biometric data—such as eye-tracking, heart rate variability, and physical interaction speed—the AI will dynamically adjust the difficulty of the simulation. If a trainee remains perfectly calm during a simulated chemical fire, the AI may dynamically introduce a secondary explosion or a blocked exit to test their advanced problem-solving skills. Conversely, if a trainee exhibits extreme stress, the system can pause and provide calming, guided remediation.
Furthermore, the widespread rollout of 5G connectivity is severing the tether of traditional VR. The massive bandwidth and ultra-low latency of 5G networks will allow incredibly complex, photorealistic 3D environments to be rendered in the cloud and streamed instantly to lightweight, standalone headsets. This technological leap is laying the groundwork for the Industrial Metaverse—a persistent network of hyper-accurate digital twins representing global manufacturing plants, offshore rigs, and hospital wings. By 2026, it is projected that spatial collaboration will be the norm, allowing a senior safety engineer in Europe to step into the digital twin of a factory in Asia to conduct a synchronized, multi-user safety audit in real-time.
Simultaneously, the democratization of VR creation will reach critical mass. The continued evolution of no-code platforms, pioneered by solutions like the RoT STUDIO License, will empower non-technical professionals across all industries to author, edit, and deploy highly complex immersive training scenarios with the ease of building a presentation. Coupled with advancements in wearable haptic suits that provide full-body physical sensations, the boundary between the digital simulation and physical reality will become indistinguishable.
Conclusion
The traditional methodologies of occupational health and safety training have reached their absolute limits. In an era where industrial complexity is soaring and the cost of human error is measured in catastrophic environmental damage and lost lives, relying on passive reading and classroom lectures is a systemic vulnerability. Health, Safety, and Environment (HSE) VR training has emerged not simply as an operational upgrade, but as a total revolution in behavioral psychology, risk management, and corporate education.
By leveraging the profound psychological impact of spatial computing, organizations can bypass cognitive overload and instill permanent, life-saving muscle memory. The ability to practice the most dangerous industrial and medical procedures in a flawlessly safe, highly analytical digital environment accelerates time-to-competency, drastically increases first-time quality, and generates immense financial returns by eliminating the logistical nightmares of traditional physical training.
To navigate this digital renaissance, enterprises must align with proven technological visionaries. With a peerless legacy extending over thirty years, RoT STUDIO remains the definitive pioneer in transforming complex engineering data into scalable, immersive human experiences. From their democratizing no-code platforms and exhaustive off-the-shelf VR catalogues to their groundbreaking advancements in visio-haptic healthcare simulations and mixed-reality disaster preparedness, they provide the ultimate ecosystem for safeguarding the modern workforce. The future of corporate safety is undeniably immersive, and the organizations that embrace this reality today will define the operational standards of tomorrow.


